
Five Ways to Stay Safe Online
The Internet has become such a vast place. It is an endless source of opportunities, information, and entertainment. However, with that significant expansion in both scope and application over the last couple of decades, the dangers it poses have also grown. From leaked passwords to hacked accounts, stolen data, and more, cyber attacks are a real threat nowadays and can, however unlikely, happen to anyone. That is why it is vital in our modern world to know how to stay safe online.
In the past, we have taken multiple steps to ensure the security of our customers: we improved our website’s login security, implemented a better malware detection and cleaning suite, and all our servers are protected by robust security measures, to name a few. However, we realised that all these steps were ones we, ourselves, took. They are only one side of the coin. The other is the person we are trying to protect. The user who logs in online, browses pages, exchanges data with other users, and generally uses the Internet. You are already well aware of why cybersecurity is vital: it protects us as users of the World Wide Web and safeguards our personal data.
We have done a lot to ensure our side of the coin is secure, but it is time we direct our efforts towards educating others on how to do it themselves. Because of that, we give you five (and a few extra) ways to protect yourself online.
Use Strong, Unique Passwords for Every Account

Passwords are undoubtedly one of the most fundamental security measures online, and they have existed for ages. However, gone are the times when passwords such as “password123” or “1234567890” were acceptable. Nowadays, most websites will tell you that such a password is not strong enough and flat-out disallow you from using it. It might seem frustrating, but trust us–it is for your own safety.
Why Password Strength Matters
Many websites now require strong passwords, and we encourage all our users to use strong passwords because they are the most straightforward way into someone’s account. Sure, you will also need a username or email address; however, those are typically much easier to obtain than a password. That is because passwords are typically stored in a much more secure fashion because they are the key to an account.
Recently, we posted a blog about the newest WordPress version. One of the major features was an upgrade to their password security system. We are mentioning it here to give you an idea of how some applications store their passwords. It is not the only method, but it is a perfect example of a robust and popular one. But, you might ask, why bother with a difficult password if it is going to be stored securely? That is a good question.
One of the most common cyber attacks nowadays is the brute force attack. As the name implies, it utilises sheer, brute force to try and guess a user’s password. It is as barbaric as it sounds. However, that is one of the major reasons why a strong password is vital nowadays. With the amount of computing power modern machines can put out, hackers can go through millions of user/password combinations quickly. A password like the one we mentioned earlier (password123) will be busted through in a matter of seconds. However, something far more complex (like G#2l$7w!Q@v9) will take much longer. We are talking years here. We compiled this table below to showcase how long it would take to crack various passwords with modern hardware.
| Number of Characters | Hardware Used | Numbers Only | Lowercase Letters | Upper and Lowercase Letters | Numbers, Upper and Lowercase Letters | Numbers, Upper and Lowercase Letters, and Symbols |
| 8 | RTX 4090 | 4 hours | 10 months | 219 years | 896 years | 2,000 years |
| 8 | RTX 5090 | 3 hours | 8 months | 172 years | 703 years | 1,000 years |
| 8 | RTX 5090 x12 | 15 minutes | 3 weeks | 15 years | 62 years | 164 years |
| 8 | A100 x20,000 (ChatGPT 4) | Instantly | 43 minutes | 1 week | 1 month | 3 months |
You can see how adding more and diverse characters to your password makes a hacker’s job that much more difficult. Yes, if someone did have 20,000 of the A100 GPU and was using ChatGPT 4’s help, they could crack difficult passwords quickly. However, we included that particular row to illustrate how ludicrous one’s setup must be to achieve any sort of “reasonable” times when cracking strong passwords.
The more diversified the symbols in the password, the more combinations there are, therefore, harder to guess and crack. Do not skimp on those symbols!
Use Unique Passwords
Another common cyber attack that is easy to prevent is the so-called credential stuffing. Unlike brute force attacks, credential stuffing does not try to force its way into a user’s account. Instead, it exploits people’s tendency to use the same password across multiple accounts. Such an attack uses already obtained credentials (username/email and password pair) to access different websites. Because most users will use the same password, since it is easier to remember, attackers can get access to all their accounts by obtaining their password only once.
Through automated tools, attackers can try countless website login pages to see if their credentials will authenticate anywhere. That is why it is imperative nowadays to use a unique password for each account online. But with how nearly every website requires us to create an account with them, the number of passwords to remember can get pretty overwhelming, especially since they also need to be “strong.”
Password Tools
Fortunately, many reliable, secure tools online can keep track of your passwords and help create them. When it comes to strong passwords, you have a couple of choices. You can think of them yourself, especially once you know what “strong” means. Alternatively, you can use a password generator.
To begin with, a password should not be less than eight characters in length. Nowadays, that is the bare minimum, but the longer the better. Next, ensure the password itself is not an actual word. It should not be a name or anything that is in any dictionary of any language. In other words, the password should be a random jumble of letters and numbers at a minimum. Symbols will make it even stronger.
There are countless password generators online, and they will all provide you with perfectly serviceable passwords. Simply type “password generator” into your favourite search engine, and you will see a ton of results. Here is one example. Just remember to keep each password wholly different from the rest. Your browser will help you keep track of them when you log in for the first time. Modern browsers have the ability to store and automatically fill in credentials.
However, we recommend using a dedicated password manager. Since password managers are developed to take care of your passwords, they are far more suitable for the task. Again, there are many options online, so the best advice we can give you here is to do some research. Look up some of the more popular managers, see what others say about them, and make an informed decision.
Simply following these few pieces of advice, you will end up with strong, secure passwords that are stored safely.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication

Two-factor authentication is another quintessential security feature that many modern websites offer or even demand. To quickly explain this feature, we need to look at its name: two-factor authentication. This type of authentication involves a two-pronged approach to access management. Most times, the first prong (factor) is a user’s password. You type it in, and then the system will ask you for your second factor, a second verification step. There are many types that exist, but these are the most common.
- Authentication App – This is easily the most common 2FA method. It involves installing an application on a mobile device. That application will provide the one-time passwords necessary for the second layer of authentication. We offer this type of 2FA to all our customers;
- SMS or Email Authentication – Similar to the previous authentication method, however, the password is instead sent to you either via SMS or email;
- Push Notifications – Some 2FA options include push notifications. A prompt appears on your device that you have to approve or deny;
- Physical Security Key – This method of authentication involves an actual, physical device that you have to plug in or scan when you try to log into your account. Typically, the size of a thumb drive, these devices hold the security keys within them;
- Biometric Authentication – Finally, users can set up a second factor using biometric data. Things like fingerprints, facial recognition, or retina scans can provide the second factor.
Most two-factor authentication online is through an app, SMS, email, or push notifications. The majority of websites offer one or all of these options. This sort of authentication is extremely easy to set up. However, it also offers an excellent way to increase the security of your accounts. You can read more about 2FA in our blog on the topic.
Be Cautious with Emails and Links

One of the easiest ways to stay safe online is to be cautious when it comes to emails or links. It is very simple: do not open or click on anything you do not trust or know the origin of. There is a very good reason for that. Email attachments and links can contain malicious scripts, for example. Links can also lead to websites that aim to illegally obtain your personal or login information, or just download a virus onto your machine the moment you visit them.
There are numerous reasons not to click on random attachments or links. Nonetheless here is a quick list of the most common ones. These should be more than enough to give you an idea of why you should be careful about what you open.
- Phishing Attacks – Phishing used to be mostly conveyed via email in the past, but text messages have also become a carrier in recent years. At its core, phishing is an attempt to obtain a user’s personal or login information illegally. Emails and texts like this often pretend to be from reputable sources (banks, for example) and urge users to give up their information via various means. Those can include logging in in order to resolve some made-up issue, giving up personal information so that some non-existent confirmation can be made, etc. Read our blog post about phishing to learn more about how it works and for more examples;
- Malware – Malware is any kind of software designed to damage, disrupt, or grant unauthorised access to a device. Attachments and links can carry such malware and install it on your system without you even noticing. Here are a few examples of what such malware can do;
- Ransomware – This type of malware can hold your files or system hostage, lock them up, until you do something specific, often paying a sum of money;
- Spyware – On the other hand, this type of malware is designed to steal your data and send or sell it to a third party without your consent. The data itself can be anything from advertisement info to your login or personal details, to flat-out tracking your entire online activity;
- Botnet – A botnet is a network of computers infected with malicious code that a third party can then control as a group. The worst part is that it is done without the user’s knowledge. Such botnets are often used to launch DDoS attacks;
- Drive-by Downloads – Sometimes links can lead to websites that automatically try to download malware to your device, without your consent. That is when a solid antivirus solution on your device is mandatory. We will touch upon those later;
- Scams – Sometimes emails or links do not necessarily contain malware, but can still be incredibly harmful. Scams are typically conducted through misdirection and misinformation. They prompt users to take specific actions that will lead to a bad decision. For example, an email might claim that an account of yours is suspended and you have to do something specific (often involving paying money or giving up your login details) to reactivate it.
As we mentioned earlier, it is super easy to protect yourself from such malware or scans. Do not trust emails simply because they look official: that is super easy to replicate. If you are suspicious of the email, then simply head to the official site and contact them directly. Ask them about the email you got to check if it is legitimate. As for links, you can always hover over them without clicking. You should see where it leads at the bottom of your browser. Here is a quick example.
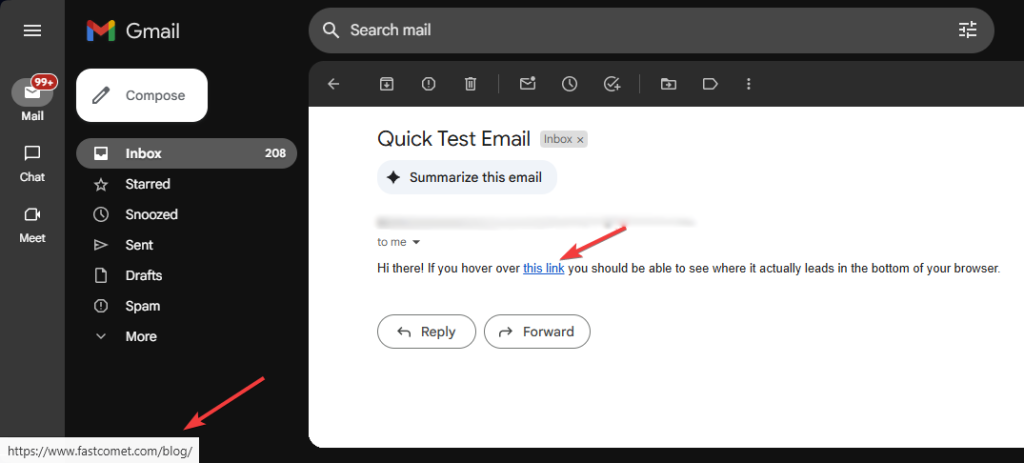
If that URL does not look legitimate to you, do not follow it. If you want to be extra certain, do not click on any attachments or links in your emails if you are not absolutely certain who sent them. Always go to the source instead and inquire there.
Keep Your Software and Devices Updated

Another thing you can do to ensure you are secure when browsing the World Wide Web is to keep all relevant software and devices up to date. There is a very good reason why software developers often put out updates to their applications. Yes, it is usually to add new features or improve existing ones. However, another major reason is to patch security vulnerabilities.
When a piece of software comes out, it usually has vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit for their malicious purposes. Naturally, developers try to patch those as much as possible prior to launch, however, the most accurate and best way to test an application’s security is to expose it to the Internet. Let us take one of the most popular Content Management Systems currently available: WordPress. On top of adding new features and polishing what is already in place, WordPress’ updates also often include security fixes to address known vulnerabilities. Not only that, the developers actually offer bounties to the community for finding such holes that need patching.
That way, there are fewer things hackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access to the application or, even worse, the device running it. What would happen if an application’s updates get neglected and those vulnerabilities no longer get fixed? As you can already imagine, those vulnerabilities can be an entry point to launch cyber attacks on the website, program, device, etc.
To that end, it is imperative you keep all your software and devices up-to-date. That is doubly true if you are working with sensitive information or have logins that another party could want. Our advice is to wait for the newest, stable version compatible with your system, then update as soon as possible. For example, you should not rush to update WordPress to the latest version the moment it comes out. Instead, wait for a bit, read up on it online, see if it is stable and compatible with your plugins and themes, and then get it.
The important thing is not to neglect your updates for too long. Letting an application become severely outdated is a major security risk. The developers are likely to fix the vulnerabilities within it in later versions. That is the same reason why many developers have specific software requirements for their applications. Going with WordPress again, it dropped support for PHP 7.0 and 7.1 with its 6.6 update in April of 2024. Due to this change, the oldest PHP version you can use with the newest WordPress releases is 7.2. Many developers follow this practice, which is not surprising.
Use Secure Connections and Avoid Public Wi-Fi

The last major piece of advice we have for you is twofold: avoid submitting personal data over public Wi-Fi networks and do not access websites that lack the proper security. In this section, we will tell you all you need to know about the dangers that public Wi-Fi networks can pose and why unsecured websites threaten your online privacy.
Caution When Using Public Wi-Fi
Using public Wi-Fi can be an alluring option when you want to browse the Internet on the go. Nowadays, many places have a Wi-Fi network, and often enough, it is free and open for anyone to connect to. While that sounds convenient, we would recommend against doing it.
The primary reason why we do not recommend using public Wi-Fi networks is that you do not know how secure they are. Most modern routers use the WPA2 security standard (or the newer but not as widely spread WPA3). However, you, as the user, still do not know if that is the case. For example, it could be an old router with an outdated security standard. You also do not know who else is on the network. Being on the same network as an attacker gives them enough information about your device to gain access to it. Since network security is an extremely expansive topic, you can check this article for more information about possible dangers lurking on public networks.
Our purpose with this post is not to scare you witless but to educate you on how to better protect yourself when out and about and ensure your devices and software are safe. To that end, if you must use a public Wi-Fi network, we recommend you do not perform any personal transactions—nothing that involves entering login credentials, banking information, card numbers, or any other personal details that you would rather not be stolen. Consider using a VPN service to protect your connection further.
Since numerous VPN providers online offer various plans, pricing, and services, we suggest researching and finding the one that most suits your needs. As to what a VPN is, it is relatively simple: it encrypts the connection you establish with a website by routing it through secure servers. That way, if anyone on the Wi-Fi network does intercept it, they will see nothing but gibberish.
Unsecured Websites Are to Be Avoided
The last thing to watch out for is websites without a valid SSL certificate. Those websites will have only http:// in the URL instead of https://. That means your connection to the website will not have encryption, so any data you send or receive will be in plaintext. If anyone intercepts said data, they can easily read it and manipulate it.
Your browser will prevent you from directly accessing such websites and warn you that the connection is not private or secure (depending on your browser). Nowadays, it is rare to see a website not secured by an SSL certificate, which makes visiting non-secured ones much more inadvisable. The warning will look something like this (screenshot is from Chrome).
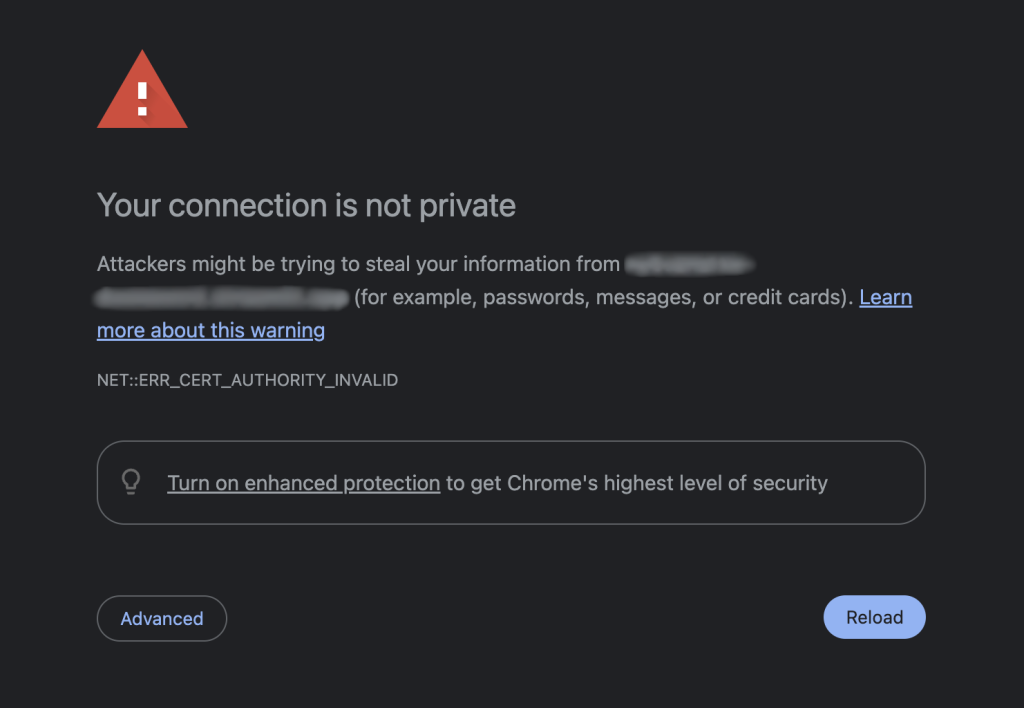
Simply put, an SSL certificate enables websites to use HTTPS. It ensures the connection between browser and server (the site’s host) has end-to-end encryption. When the connection has encryption like that, even if a malicious party intercepts it, they cannot easily read or manipulate it. If you see a website that does not have https:// in its URL, we recommend you stay away.
As for what SSL certificates, HTTP and HTTPS are, you can read up on those terms in our Knowledge Base, where we go over all the details you need to know.
Bonus Round: 5 Quick Tips to Stay Even Safer Online

All the advice for staying safe online we discussed so far should be more than sufficient for any everyday user. However, if you want to be even more secure, we have prepared a quick little list of five additional things you can do. These are not mandatory, but we still recommend them if you work with sensitive information, have data that would warrant being stolen, or want to be that much more secure online.
Here are five quick tips for being even safer online without further ado.
- Lock Your Devices – Always lock your devices when you are not using them. That is especially important for phones and tablets since leaving them unattended is much easier. Nobody other than you should have access to your devices;
- Avoid Oversharing Personal Info – Whether it is on social media, via email, voice chat, or text messages, you should always avoid talking too much about your personal information. Unless whomever you are talking to needs to know that personal information, we recommend not sharing it at all. Privacy is a huge boon of the Internet, use it;
- Clear Cookies and Browser History – No matter which browser you prefer, you should clear its cookies and history regularly. It is a good practice to boost online privacy and security. Personal data can be leaked, and some third-party cookies are not as secure as they could be, so deleting everything once in a while is a good practice;
- Consider an Antivirus Solution – This piece of advice is highly device-dependent and perhaps directed mostly at computer users. A solid antivirus suite can bolster your online security and prevent bad things from happening. On the other hand, a mobile phone or tablet might not need such a solution if you only install applications from reputable sources and follow the rest of the advice in this post. Still, there are mobile solutions as well, if you want that extra layer of security;
- Check Activity Logs – Activity logs are a great way to keep track of what your accounts are doing online. They can tell you what that account has been up to in detail, in case you suspect any shady behavior. For example, Facebook has a detailed activity log (click on your profile picture, then Settings & Privacy > Activity Log) that shows everything the account has posted, watched, searched for, etc. Great way to find out if someone else has been up to no good.
With these five extra tips, your time online should be even safer than before without requiring much extra effort. Consider them if you feel you need the extra protection and if they are convenient.
Stay Safe Out There
Without a doubt, online security is a huge topic nowadays. With technology advancing at such rapid rates, opening new avenues for devices to get hacked, it can feel daunting and impossible. However, through the tips we described above, any of our everyday users should be able to stay safe and sound online, without disrupting their browsing experience. Avoid shady websites, always make sure your apps are up to date, use strong passwords and 2FA, and stay off that enticing public Wi-Fi as much as possible. As for us here at FastComet, we will continue our quest to ensure your safety from this side of the Internet.

The latest tips and news from the industry straight to your inbox!
Join 30,000+ subscribers for exclusive access to our monthly newsletter with insider cloud, hosting and WordPress tips!
No Comments