What Are the DKIM, DMARC and SPF Records and How to Enable Them?
Updated on May 10, 2023
Nowadays, the majority of spam emails have fake data in the ‘from' field. Spammers and fraudsters use special tools to send their mail on behalf of the real owner of the e-mail address. To reduce spam, you can use just three records in your Domain Name System (DNS). These are SPF DMARC and DKIM records. The records reduce spam and improve email delivery in a different way.
Email is the most utilized channel for targeted cyber attacks,and presents the biggest opportunity for hackers to crawl into your network and get a foothold.
In 2021, more than 80% of reported security issues were the result of phishing attempts. In line with CISCO's 2021 Cybersecurity Threat Trends research, phishing accounts for nearly 90% of data breaches. With 65% of all phishing attacks being spear phishing, it is the most prevalent kind of attack. Employees get an average of 14 phishing emails per year, according to a 2021 Tessian study. And between May and August 2021, email-based attacks rose 7.3%, according to ESET's 2021 research. 24 percent of the over 467,000 successful cyberattacks in 2019 were launched through emails, according to the FBI. Cyberattacks via email frequently begin with uncomplicated, innocent-looking email communications.
However, you can defend your business and yourself from these attacks by combining SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records. What are they, and how are the records configured? Come, let's find out.
This post includes:
- What are SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Records
- Sender Policy Framework (SPF) Explained
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) Record Explained
- DMARC (Domain-based Messaging and Reporting Compliance) Record Explained
- Why configure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records?
- How to set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC?
- Conclusion
What are SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Records
Some of the most popular DNS entries for email accounts that provide security against email phishing and spoofing are SPF, DMARC and DKIM.
Together, they identify forged sender addresses and verify emails that have been sent. Let's immediately clarify the definitions of these terminologies.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) Explained
SPF, or Sender Policy Framework, is a security tool that is used to prevent email spoofing and to notify the recipient that an email is coming from an authenticated address rather than a forged one. To ensure that the recipient is receiving authenticated communications, SPF communicates with the DNS (Domain Name System), which acts as the Internet's equivalent of a phone book, connecting web browsers with websites.
SPF is configured by including it in your DNS. As a result, whenever you send an email, the recipient's DNS will check its list of SPF to see if your SPF is included. By doing so, the recipient ensures that no one is harmed and that the email exchange is nothing less than genuine communication.
Advantages and Potential Drawbacks of SPF
SPF is effective in preventing phishing. Without it, your email address would be accessible to spammers who could change it. When SPF is enabled, the receiving server's SPF protection detects and marks emails sent from your address as invalid. Using SPF demonstrates your company's commitment to defending against online threats, which benefits your sender reputation.
When a user outside of your domain forwards an email sent by you, a mismatch between the IP record and the SPF record may prevent delivery. Mail exchange and transfer agents are currently using the Sender Rewriting Scheme (SRS) to improve the deliverability of email forwards. The SPF record must also reflect any changes in third-party email service providers in order to maintain deliverability.
How SPF Works
SPF email creates a means for receiving servers to confirm that incoming email from a domain was delivered from a host approved by that domain's administrators at the most fundamental level. The SPF process is broken down into the three steps below:
The policy describing mail servers that are allowed to send email from that domain is published by a domain administrator. The SPF record for this policy is part of the overall DNS records for the domain.
An inbound mail server checks DNS for the bounce (Return-Path) domain rules when it receives an incoming email. The inbound server then makes a comparison between the approved IP addresses listed in the SPF record and the mail sender's IP address.
The receiving mail server then decides whether to accept, deny, or otherwise flag the email message based on the rules given in the transmitting domain's SPF record.
By setting up an SPF record, you will get one step closer to ensuring that valid email sent from your domain is correctly delivered to consumer inboxes.
DKIM can be used to confirm that an email message was sent from a trusted mail server in this situation.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) Record Explained
DKIM, which stands for Domain Key Identified Mail, is another method for email authentication. It uses an encrypted signature to confirm that the email sender is who they say they are, and it provides the recipient with a key to check the sender's DNS record. If DKIM is enabled, the recipient's DNS may verify the sender of the email and ensure that no fraud has occurred.
DKIM is an additional step in the email authentication process. DKIM, as opposed to SPF, assigns a domain name to your message and uses cryptographic techniques to validate it as the recipient receives it. They use a digital signature to identify the IP address.
DKIM serves the same function for all users of email services for all the same reasons as SPF does. The primary issues that DKIM addresses are email verification and authentication, providing spam-free user-friendly communication services to the sender and recipient of the email.
Note
DomainKeys(DK) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) are separate things.
Advantages and Potential Drawbacks of DKIM Authentication
The main advantage of using DKIM email is that it protects against phishing and spoofing attacks. The authentication is visible within the message itself to prevent forgeries and protect users from responding to fraudulent emails containing sensitive personal information. Spoofing and phishing protection is beneficial because they both have the potential to harm your sending reputation and future deliverability.
When it comes to message forwarding, using DKIM when creating emails has the same potential disadvantage as using SPF. A receiving server, for example, may flag an email that automatically transfers from a work computer to a user's mobile device as fraudulent. Many well-known email systems have addressed this issue. Another potential issue is a DKIM that is too short in length. Longer keys are more commonly supported. As a result, shorter ones may fail authentication.
How DKIM Works
Simply put, DKIM functions by including a digital signature in the email message headers. The organization's DNS entry contains a public cryptographic key that can be used to verify this signature.
A cryptographic key is published by the domain owner. In the domain's overall DNS record, this is specially formatted as a TXT record.
An outbound mail server creates and adds the distinct DKIM signature to the message header after the message has been transmitted.
The inbound mail servers employ the DKIM key to identify and decrypt the message's signature, after which they compare it to a brand-new version. The message may be proven to be valid and unchanged in transit and, as a result, cannot be forged or altered if the values match.
DMARC (Domain-based Messaging and Reporting Compliance) Record Explained
The technology called DMARC (Domain-based Messaging and Reporting Compliance) is effective in preventing phishing and combating email spoofing. In particular, it safeguards against the scenario where a phisher forges the Display From address (also known as 5322. From email address). By examining both SPF and DKIM, DMARC safeguards users by determining whether either domain corresponds to the domain in the Display From address.
A very basic DMARC record looks like the following:
_dmarc.example.com 14400 TXT v=DMARC1;p=none;sp=quarantine;pct=100;rua=mailto:[email protected]Why configure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records?
As you may know, if mail service is unauthenticated, you can face the following issues:
- emails you send are delivered to Spam/Junk folders
- emails you send bounce with "SPF record failure" error
- your Inbox gets numerous "Failed delivery" bounce backs of the emails you never sent
In the first case, the recipient mail server looks up the SPF record for your domain, and if it is not added, it does not match the actual outgoing server IP address, such a mail delivery will fail. Such a checking mechanism is implemented in order to make sure email comes from a legitimate sender and verified sender.
The second situation takes place when there is no SPF/DKIM configured for your domain or they are configured incorrectly, which enables the unauthorized party to forge emails using @yourdomain.com mailbox. Such cases are called mail spoofing.
Email Deliverability is an effective set of anti-spoofing and anti-spamming tools available in cPanel.
The Email Deliverability table displays your cPanel account's domains and allows you to address any existing problems with your mail-related DNS records – SPF and DKIM.
How to set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC?
FastComet Shared Hosting plans are created with DKIM and SPF records by default, and those records cover all domains on the hosting plan. While configuring SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records, you need to follow the correct order, which can be found in Google Workspace Admin Help. Keep in mind that the initial configuration of DKIM, SPF, MX, and DMARC as well as any later updates must be made in the proper sequence.
The default settings for all domain providers are listed below (using Google as an example). But keep in mind that each of your domains might be set up differently because you have your own.
General DKIM and SPF setup
Log into cPanel → Email section → Email Deliverability menu:
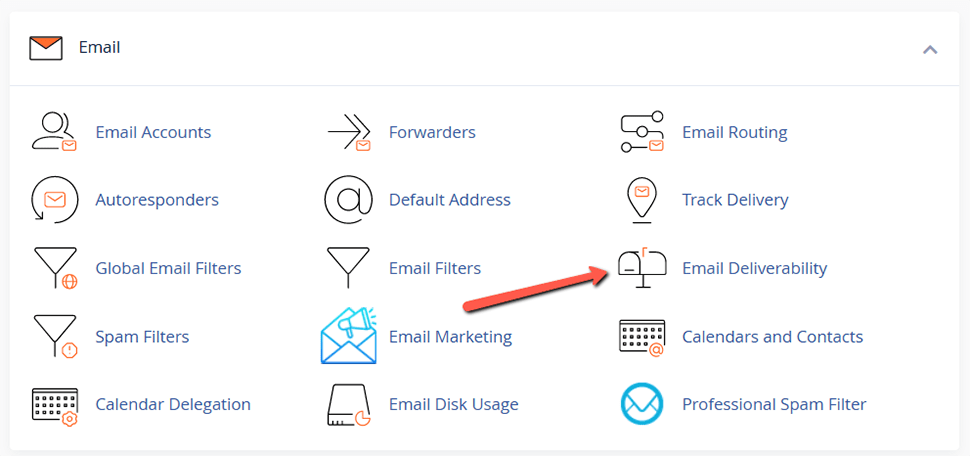
This section allows you to perform the following actions:
Repair - this feature allows the system to repair a domain's invalid records:
Notes
- If the system does not manage the DNS records for the domain, this option is not available. As a result, you can only utilize the Repair option if your domain is linked to our shared hosting nameservers.
- Two or more domains with records in the same zone cannot be updated at the same time. Only when domain records are located on separate zones is a bulk records update possible.
- The repair procedure is not interrupted by reloading the interface.
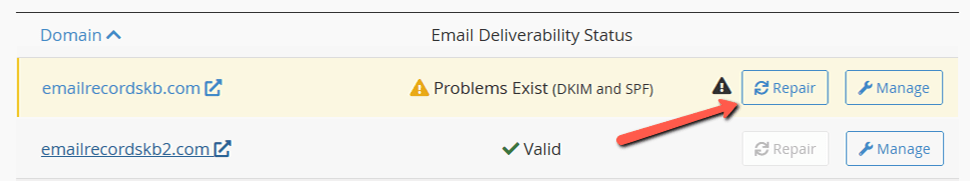
You can evaluate and accept the system's suggestions for any invalid records in the window that displays after clicking Repair. Before you give your approval for the system's repairs, you can also Copy or Customize a proposed record. When you select Repair, the entries are automatically added to the domain's or subdomain's DNS zone.
This process can take up to five minutes, depending on the server. When the records are set up, you will receive a corresponding success message.
Allow some time to pass for the records to propagate and refresh the page afterwards. The Email Deliverability Status will be then changed to Valid:
2. Manage - this option allows you to manually configure a domain's mail-related DNS records.
The DKIM and SPF record data are already displayed in the Manage the Domain section. Therefore, you typically only need to manually copy them and put them into your domain's DNS zone. Alternatively, you can choose to automatically add the SPF and DKIM records to the DNS zone by selecting Install the suggested record:
Note
The Install the suggested record option is available only in case your domain name is pointed to our Shared hosting nameservers.
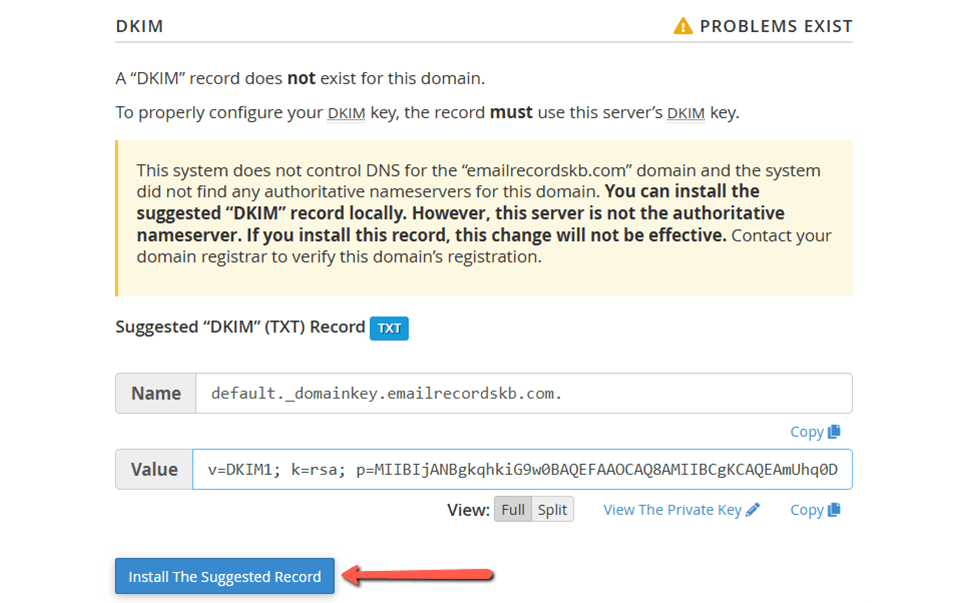
After the record is installed, you will receive the confirmation message.
In the SPF section, you will also have an option to Customize the system's recommended SPF record for a domain.
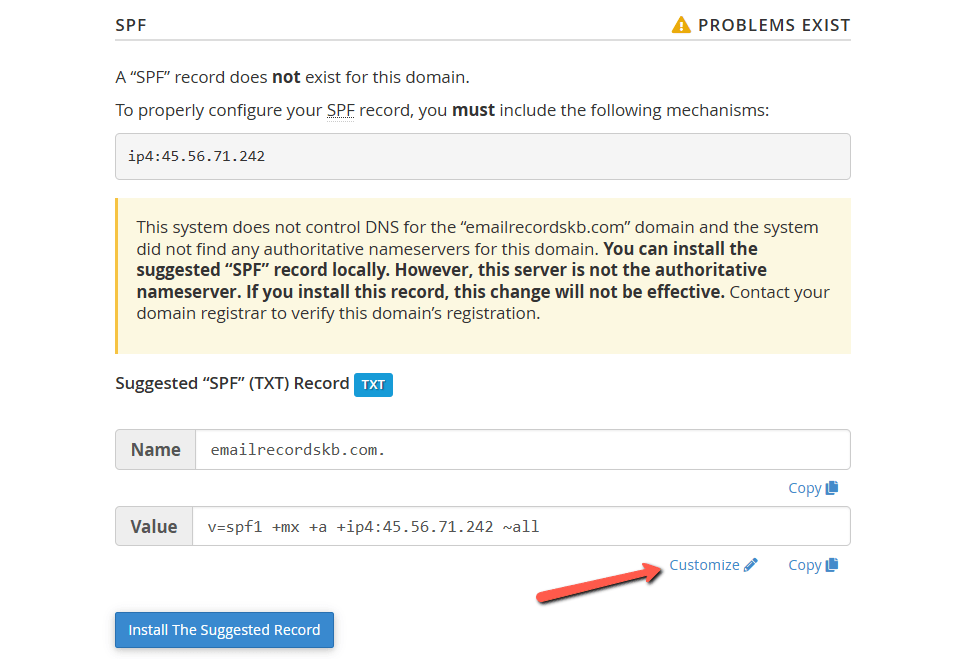
The interface displays the domain's current SPF name and value in the Current "SPF" (TXT) Record section, if one exists, and the system's recommendations in the Suggested "SPF" (TXT) Record section:
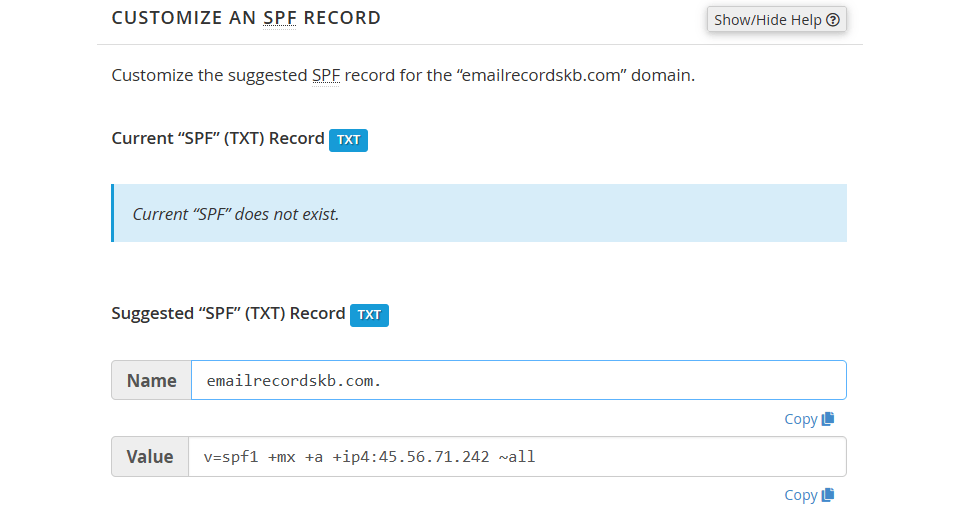
You can configure the following settings:
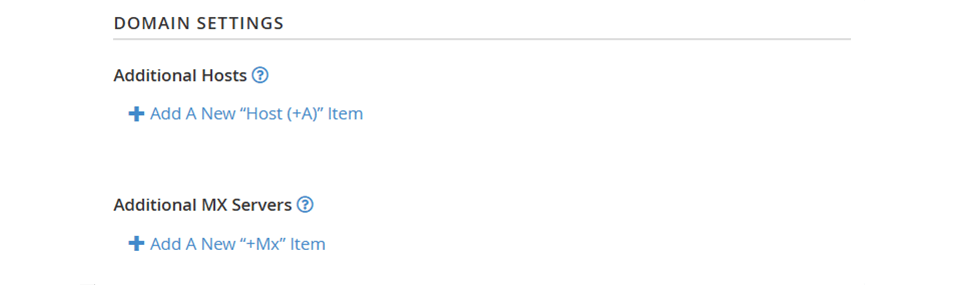
1. Domain Settings - this section allows you to define the hosts or MX servers allowed to send mail from your domain:
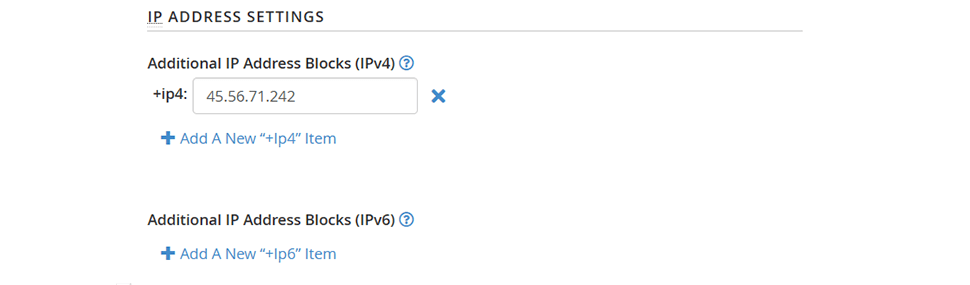
2. IP Address Settings - You can add further IP address blocks to your SPF record using this section. The system automatically adds the primary IPv4 or IPv6 addresses of your server to these lists:
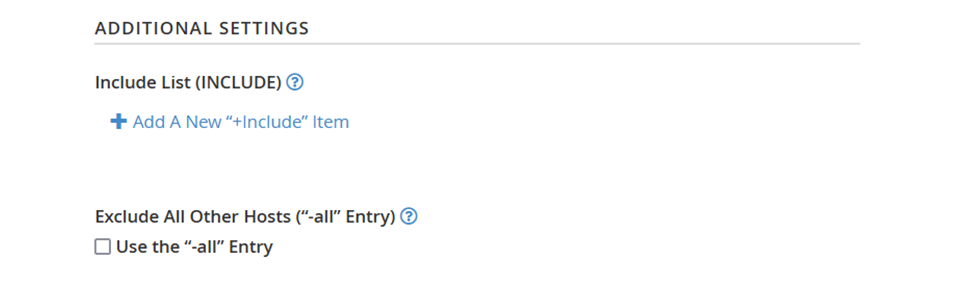
3. Additional Settings - You can change more SPF record settings in this area.
4. Preview of the Updated Record - Based on its current revisions, this section depicts what the modified SPF record would appear like. To set up the fresh record, click on the Install a Customized SPF Record button:
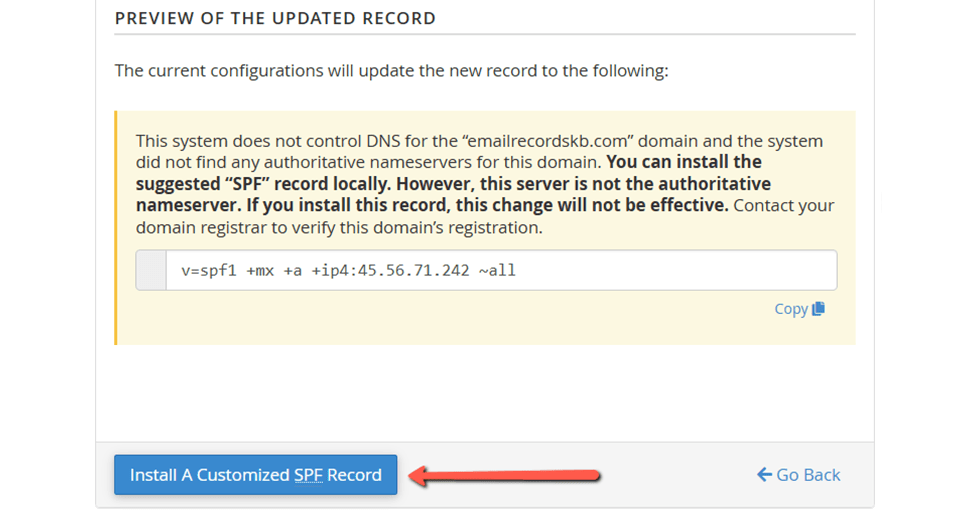
That's it!
General DMARC setting
Just like SPF and DKIM, DMARC is a simple one-line entry in your DNS records.
Before setting it, make sure you've configured SPF and DKIM records for the required domain.
Then follow these steps:
- Go to your DNS settings and create a new record via the drop-down menu → Add "TXT" Record.
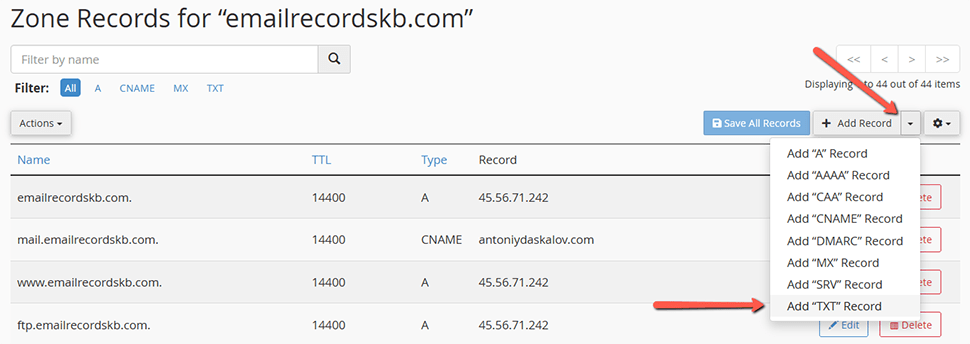
- Add the hostname (for example,
_dmarc):
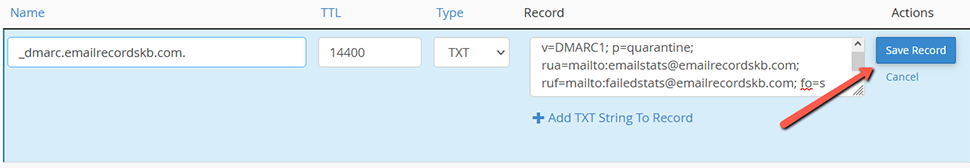
- Add the value. You can find a sample DMARC entry that you can use to create your own below:
v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; rua=mailto:[email protected]; ruf=mailto:[email protected]; fo=sWhere:
- v - A mandatory tag-value (don't change it!).
- p - Mail processing policy. One of the possible options is specified - none, quarantine, or reject.
- rua – Email address for receiving statistical reports. The address must belong to the same domain for which the DMARC record is configured.
- ruf - Email address for receiving reports on failed authentication checks. Since each error when verifying the sender's address generates a separate report, it's better to have a separate mailbox for this.
- fo - Determines in what cases reports will be sent to the domain owner. Possible values include:
- 0 - a report is sent if SPF and DKIM checks fail. Set by default.
- 1 - a report is sent if one of the checks fails - either SPF or DKIM.
- d - a report is sent for each DKIM verification performed.
- s - a report is sent for every SPF check performed.
There are also online checkers and generators for DMARC records, which you can use if you do not wish to create the record manually.
Conclusion
If your company sends transactional or commercial emails, you must use SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. SPF and DKIM ultimately help to protect your consumer interactions and brand reputation while protecting your company from phishing and spoofing attacks. Remember that these are just a few steps you can take to ensure that your clients' time-sensitive emails arrive in their inboxes on time and are not routed to spam folders.
In a nutshell, SPF allows email senders to specify which IP addresses are permitted to send mail for a specific domain. DKIM's encryption key and digital signature, on the other hand, confirm that an email message has not been falsified or altered. Furthermore, to protect users, DMARC examines SPF and DKIM to determine whether either domain corresponds to the domain in the Display From address.
Authentication by itself does not guarantee the quality of your content. Use proper email etiquette and best practices for inbox placement; spamming content may result in complaints and unsubscribe requests even when verified.
When you use these email authentication techniques correctly, you will be one step closer to increasing your email deliverability and delivering secure emails that generate revenue for your company.
We hope you find this article useful. Discover more about FastCloud - the top-rated Hosting Solutions for personal and small business websites in four consecutive years by the HostAdvice Community!

SSD Cloud Hosting
- Free Domain Transfer
- 24/7 Technical Support
- Fast SSD Storage
- Hack-free Protection
- Free Script Installation
- Free Website Transfer
- Free Cloudflare CDN
- Immediate Activation